HIP DYSPLASIA
HIP DYSPLASIA
When ball and socket joint of hip is not aligned in its position, it is said to be dislocated and the condition is known as hip dysplasia. If the condition is brought to attention at an early stage, can be treated with a soft support (brace). In adults or older cases, surgery may be needed.
Symptoms
Infants: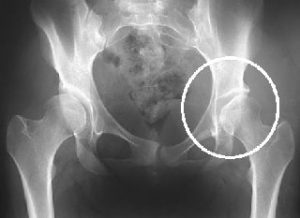
- Low flexibility in one leg
- One leg is shorter than the other.
- Limp while walking (in children).
Adults:
- Tear in hip tissue
- Osteoarthritis
- Groin pain, depending on activity
- Instable hip joint
Causes
The causes include:
- Less space inside the uterus due to breech presentation, macrosomia or 1st pregnancy leading to dislocation of the joint from its actual position.
- The ball of thigh bone not seating completely inside the socket, hence resulting in superficial alignment of the joint.
Diagnosis
Early evaluation of hip joint fitting into position is necessary. A doctor is required to assess the baby by moving joint in all directions during its initial visits. Some milder cases do not come to attention and appears in adulthood. Imagings such as X-rays and MRI are often required.
Treatment
Depends on the age of the person
Infants: usually treated with Pavlik harness. For babies above 6 months, a full-body cast is used after alignment. Some children require surgery.
Older individuals: Hip replacement surgery is an option.
