Roseola
Roseola
It is usually a mild infection that affects children by age 2. It sometimes can affects adults. This is a commonest type of infection that most of the children have been infected by the time they enter kindergarten. Roseola is caused by two common strains of herpes virus.
Symptoms
Symptoms of roseola appears usually after a week or two after getting infection. But this condition can also be asymptomatic. Patient with roseola presents with: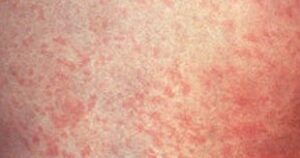
- Sudden, high grade fever along with sore throat, runny nose or cough
- Rashes appear when fever subsidies and usually consists of small pink spots and patches. Rashes usually starts from abdomen and then spreads to the neck and arms
- Children become irritable
- Mild diarrhea
- Loss of appetite
- Eyelid swollen
Causes
Usually the commonest cause of this infection is human herpes virus 6, but it can also be caused by human herpes virus 7. Roseola is transmitted from person to another person through infected saliva or secretions. Roseola, even in the absence of rashes is a highly contagious disease. Unlike other viral illnesses that have relatively rapid spread, roseola rarely results in an outbreak.
Complications
Usually complications are rare with roseola but it can become complicated in low immunity people such as:
Diagnosis
Diagnosis depends upon detailed medical history and complete general physical examination of the patient. Along with this examination for rashes is very crucial as telltale rash is present in roseola patient. Antibodies to roseola can also be detected in blood test.
Treatment
Usually roseola is a self-limiting infection. Over-the-counter medications for fever such as acetaminophen (Tylenol, others) or ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin, others) can be prescribed. Aspirin should be used with caution as it is linked to a life-threatening condition in children, Reye’s syndrome. Antibiotics are not given. Antiviral drugs such as acyclovir can be prescribed in patients with low immunity.
Lifestyle and home remedies
- Lot’s of rest
- Drink plenty of fluid and electrolyte rehydration solution (Pedialyte, others)
- Sponge baths
